Sound Attenuation
Industrial Noise Control Studies
Study different equipment noise and recommend suitable noise insulation/reduction. This include diesel generators, gas turbines, compressors, pumps, fans, chillers, factory machinery, traffic noise,...etc. Our evaluations and recommended solutions meet general guidelines and practices of international standards and noise laboratories such as ASTM E477, ASTM E90, ISO 140, ISO 7235, Sound Research Laboratory (SRL) and others. Our services extend to design or verifying others design to meet the specified noise rating (NR) or noise criteria (NC). All our studies are done in accordance with the known international standards like: ISO 6798, ISO 8528-10, ISO 3746,..
Study different equipment noise and recommend suitable noise insulation/reduction. This include diesel generators, gas turbines, compressors, pumps, fans, chillers, factory machinery, traffic noise,...etc. Our evaluations and recommended solutions meet general guidelines and practices of international standards and noise laboratories such as ASTM E477, ASTM E90, ISO 140, ISO 7235, Sound Research Laboratory (SRL) and others. Our services extend to design or verifying others design to meet the specified noise rating (NR) or noise criteria (NC). All our studies are done in accordance with the known international standards like: ISO 6798, ISO 8528-10, ISO 3746,..
|
Anechoic Room in the Royal Institute of Stockholm (KTH). Professor Mats Abom is explaining to the visitors the different functions of the room in measuring different acoustic parameters of different industrial acoustics.
|

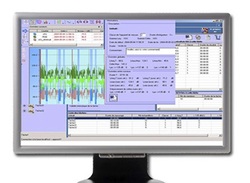
NEC Acostix ™ Software
NEC Acostix software is a programmable spreadsheet based software developed by Najah Engineering Consultants to help design engineers, consulting engineers and manufacturers to design acoustic enclosures, noise barriers, and acoustical rooms and do various acoustics calculations. It also helps them verify if existing designs can conform to the noise rating specified by the customers. Upon request, the software can be customized to suit different customer's business requirements. Click to see more details.
NEC Acostix software is a programmable spreadsheet based software developed by Najah Engineering Consultants to help design engineers, consulting engineers and manufacturers to design acoustic enclosures, noise barriers, and acoustical rooms and do various acoustics calculations. It also helps them verify if existing designs can conform to the noise rating specified by the customers. Upon request, the software can be customized to suit different customer's business requirements. Click to see more details.
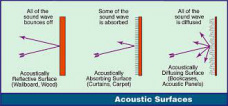
Acoustic Walls and Noise Barriers:
We design and verify the design of walls and barriers used to block noise from different sources. Walls can be used as part of acoustic enclosures or for buildings. Determining the sound reduction index (SRI) or transmission loss (TL) of the wall is a major objective to block the noise to meet the specified noise rating or criteria.
We design and verify the design of walls and barriers used to block noise from different sources. Walls can be used as part of acoustic enclosures or for buildings. Determining the sound reduction index (SRI) or transmission loss (TL) of the wall is a major objective to block the noise to meet the specified noise rating or criteria.

Rectangular Air Duct Attenuators:
Attenuators are inserted in the air duct systems to attenuate the sound level to meet the specified noise rating or criteria. Sound attenuators attenuate the sound but they cause considerable pressure drop to the air flowing through them. This pressure drop must be carefully and precisely calculated to ensure the duct airflow is smooth and in the same time, the sound is attenuated. The attenuators have many design parameters such as the number of splitters in the duct, the thickness of the splitters, the air gap between them, the aperture height and width, the attenuator duct length, type and density of acoustic filling used in the splitters, perforation configuration and air flow rate. When air flows in the ducts it generates noise, which could also be considerable if the airflow speed, is high. Attenuators are acoustically sized using insertion loss (IL) measured in dB across the octave band frequencies. Aerodynamically it is sized in terms of pressure drop at certain airway velocity. Typically, this should not exceed 120 Pa diesel generators and for most of the systems.
Attenuators are inserted in the air duct systems to attenuate the sound level to meet the specified noise rating or criteria. Sound attenuators attenuate the sound but they cause considerable pressure drop to the air flowing through them. This pressure drop must be carefully and precisely calculated to ensure the duct airflow is smooth and in the same time, the sound is attenuated. The attenuators have many design parameters such as the number of splitters in the duct, the thickness of the splitters, the air gap between them, the aperture height and width, the attenuator duct length, type and density of acoustic filling used in the splitters, perforation configuration and air flow rate. When air flows in the ducts it generates noise, which could also be considerable if the airflow speed, is high. Attenuators are acoustically sized using insertion loss (IL) measured in dB across the octave band frequencies. Aerodynamically it is sized in terms of pressure drop at certain airway velocity. Typically, this should not exceed 120 Pa diesel generators and for most of the systems.

Acoustic Louvers:
Acoustic louvers are used in buildings to handle large volume of airflow inlet or discharge while keeping the noise within the specified noise rating or criteria. Louvers are less deep than attenuators and they are cosmetically more suitable for residential and commercial buildings. Louvers can have different shapes. The shape of the louvers affect the airflow and in the same time dictates the sound transmission loss (STL). The STL is normally used to indicate the louvers acoustical performance. Acoustical treatment of louvers can include acoustic materials filling covered by perforated steel or aluminum sheet. The louvers should be designed to achieve the required STL and in the same time to allow the volume of air to flow without exceeding the maximum allowable pressure drop.
Acoustic louvers are used in buildings to handle large volume of airflow inlet or discharge while keeping the noise within the specified noise rating or criteria. Louvers are less deep than attenuators and they are cosmetically more suitable for residential and commercial buildings. Louvers can have different shapes. The shape of the louvers affect the airflow and in the same time dictates the sound transmission loss (STL). The STL is normally used to indicate the louvers acoustical performance. Acoustical treatment of louvers can include acoustic materials filling covered by perforated steel or aluminum sheet. The louvers should be designed to achieve the required STL and in the same time to allow the volume of air to flow without exceeding the maximum allowable pressure drop.
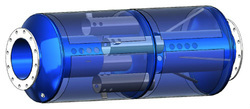
Exhaust Systems Silencing:
This includes the silencing of high speed exhaust gases with pulsating noise. Diesel generators exhaust silencers are good example of these silencers. Silencers are acoustically designated by what is known as grade. Grades can be found to be from industrial grade with only 10-15 dB attenuation up to super hospital grade silencers with up to 50-55 dB attenuation. The silencers are also sized with respect to their exhaust flow capability. This is designated in terms of silencer pipe diameter. To select the suitable silencer you should know the engine exhaust noise level (exhaust noise spectrum) and you should have noise rating or criteria, which you should not exceed. NEC can assist you to calculate the suitable silencers for the application and design reactive and dissipative mufflers in accordance to ASHRAE and other international standards.
This includes the silencing of high speed exhaust gases with pulsating noise. Diesel generators exhaust silencers are good example of these silencers. Silencers are acoustically designated by what is known as grade. Grades can be found to be from industrial grade with only 10-15 dB attenuation up to super hospital grade silencers with up to 50-55 dB attenuation. The silencers are also sized with respect to their exhaust flow capability. This is designated in terms of silencer pipe diameter. To select the suitable silencer you should know the engine exhaust noise level (exhaust noise spectrum) and you should have noise rating or criteria, which you should not exceed. NEC can assist you to calculate the suitable silencers for the application and design reactive and dissipative mufflers in accordance to ASHRAE and other international standards.
